The roots of training, development, and organization development (OD) can be traced back to the very beginnings of education itself. Exploring the history of education reveals a continuous journey of human advancement—starting with learning driven by the need for survival; evolving into education inspired by ancient traditions, classical works, and religious principles; influenced further by the impact of warfare and military strategies on scientific and technical studies; transitioning into job skills training and the scientific management approaches of the industrial revolution; advancing to leadership development initiatives and team training in the post–World War II period; and culminating in programs aimed at fostering growth in individuals, organizations, and communities for diverse work-related objectives. While training and development and organization development (OD) share common ground, they are regarded as distinct areas of practice. This chapter specifically focuses on the early history of training and development within the context of the United States.
Emergence of training & Development
Training and development in the United States gained prominence during and after World War II, driven by the need for skilled workers to support the growing wartime economy and technological advancements. Additionally, the rise of the U.S. labor movement during this time played a key role in fostering the growth of employee training initiatives
World War II, Training Within Industry (TWI)
The emergence of training and development after World War II was significantly influenced by the Training Within Industry (TWI) service, which partnered with the U.S. War Manpower Commission to support wartime production. TWI trained millions of workers and supervisors, established programs in thousands of manufacturing plants, and introduced new methods like the four-step job instruction program. Even after its closure in 1945, TWI's impact persisted, contributing to the establishment of training as a permanent fixture in companies and leading to the rise of the training director profession. The American Society of Training Directors, founded in 1945, laid the groundwork for modern HRD associations like ASTD and ATD.
The Servicemen's Readjustment Act of 1944 (G.I. Bill) also shaped post-war training and education by providing returning soldiers with benefits like college tuition and vocational training. This led to significant growth in education and job training programs, with millions of veterans benefiting from these opportunities.
Industries further adopted training methods from the war, including the Instructional Systems Development (ISD) model, which introduced a systematic approach to training with five phases—analyze, design, develop, implement, and evaluate (ADDIE). This model evolved over the decades, incorporating refinements and adaptations for diverse settings, such as workplaces and laboratories. Structured on-the-job training also became popular for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Despite widespread use, calls for improvements to training approaches, including reducing analysis time and better integration with work, continued into the late 20th century
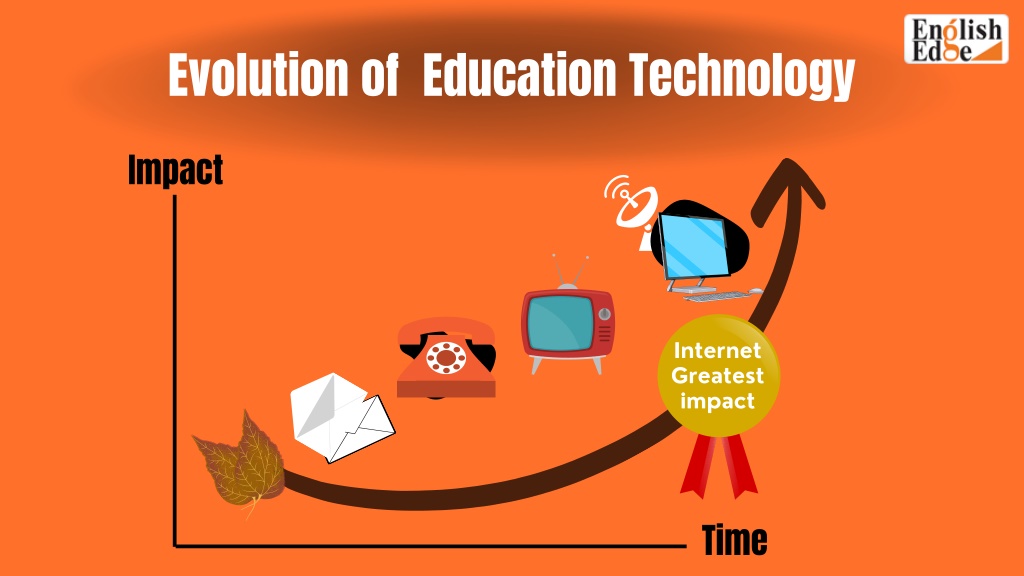
The emergence of systems for training and instructional technology
Represents a significant shift in the way education and skill development are approached. These systems harness the power of technological advancements to improve how knowledge is delivered, absorbed, and retained, catering to a wide range of learning styles and needs. Below is an overview of this transformative journey:
Traditional Roots: Initially, training and education were heavily reliant on instructor-led, classroom-based methods. Tools were limited to physical materials such as textbooks, chalkboards, and printed charts.
Digital Shift: The advent of computers and the internet marked the beginning of the digital revolution in education. E-learning platforms emerged, introducing multimedia content like videos, animations, and interactive simulations, making learning more engaging and accessible.
Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms such as Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas brought a new level of organization to education. These systems allowed educators to manage courses, track student progress, and assess performance more effectively.
Personalized Learning: With the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics, adaptive learning systems were developed. These platforms tailor educational content and pacing to individual learners, enhancing both engagement and outcomes.
Mobile Learning (M-Learning): The rise of smartphones and tablets enabled learners to access educational content on the go. This shift introduced greater flexibility, allowing learning to happen anytime, anywhere.
Gamification and Immersive Technologies: The use of game-like elements and immersive tools such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) has made learning more interactive and effective. These technologies are particularly impactful in fields requiring hands-on experience, such as medicine, engineering, and military training.
Collaborative Tools: The rise of platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Classroom has emphasized the importance of collaboration and communication in learning. These tools became essential during the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling remote learning and virtual classrooms.
Future Trends: The future of instructional technology is being shaped by innovations such as AI, machine learning, blockchain for credentialing, and the development of the metaverse. These advancements aim to create more inclusive, immersive, and secure learning environments, further transforming the educational landscape.
Influence of Vocational Education
Vocational education holds significant influence in shaping individuals, communities, and economies by equipping learners with practical skills and training tailored to specific trades or industries. Here's a closer look at its impact:
|
Aspect
|
Impact
of Vocational Education
|
|
Economic
Empowerment
|
-
Connects learners to industry needs, enabling faster employment.
|
|
-
Reduces unemployment and contributes to economic growth by addressing labor
market demands.
|
|
Skills
Development
|
-
Provides hands-on training in fields like healthcare, technology,
construction, and hospitality.
|
|
-
Equips learners with job-specific skills, creating a more skilled workforce.
|
|
Inclusion
and Opportunity
|
-
Targets diverse groups, including marginalized communities, promoting
inclusivity.
|
|
-
Offers alternative pathways for those not pursuing traditional academic
education.
|
|
Career
Progression
|
-
Provides a strong foundation for career growth.
|
|
-
Includes pathways for certifications, further learning, or transitioning to
higher education.
|
|
Innovation
and Entrepreneurship
|
-
Fosters creativity and practical problem-solving skills.
|
|
-
Prepares graduates to start businesses or bring innovative solutions to their
fields.
|
|
Global
Competitiveness
|
-
Strengthens industries and enhances global competitiveness.
|
|
-
Bridges the gap between education and employment, meeting international
standards.
|
|
Social
Impact
|
-
Boosts confidence, dignity, and independence by enabling individuals to earn
a livelihood.
|
|
-
Contributes to community development and improves societal well-being.
|
Human Capital Theory and the Economic Value of Training

Human Capital Theory emphasizes that investing in education, training, and skill development enhances an individual's economic potential and contributes to societal growth. Here's how training contributes to economic value:
Increased Productivity: Training equips individuals with advanced skills and knowledge, leading to better efficiency, innovation, and higher quality in their work. This improved productivity benefits organizations and economies.
Economic Growth: A well-trained workforce leads to technological progress and industrial development. Countries with strong human capital investment tend to experience sustained economic growth and global competitiveness.
Higher Earnings and Prosperity: For individuals, training increases employability and earning potential. It empowers people to secure better opportunities and improve their standard of living.
Adaptability to Change: Training ensures workers can adapt to technological advancements and shifting market demands, maintaining relevance in an ever-changing economic landscape.
Reduction in Unemployment: By matching skills with industry needs, training reduces skill mismatches and lowers unemployment rates, fostering economic stability.
Social Benefits: Beyond economics, training enriches communities by empowering individuals to contribute meaningfully, reducing inequality, and fostering social cohesion.
Gary Becker and Theodore Schultz highlighted that human capital investments are as crucial as investments in physical capital, such as machinery or infrastructure. Together, they underline the transformative power of education and training in driving both individual and collective progress
Employee Training—From Classroom to Computer to Realistic Context
Corporation (factory) schools originated in the early 1900s to meet the demand for skilled workers in industrial production. These schools emphasized classroom training as a more efficient alternative to on-the-job training, as it minimized production disruptions and allowed one instructor to train many workers.
Over time, as work became more complex, and expectations of workers shifted toward understanding entire operations rather than isolated tasks, advances in instructional technology began to transform training methods. By the 1980s, innovations like the Instructional Systems Design (ISD) model, on-the-job training enhancements, videos, and simulations began shaping training practices.
The 1990s saw the widespread adoption of computer-based training, driven by its speed, interactivity, and accessibility to multiple learning resources. Tools like Electronic Performance Support Systems (EPSSs) and Automated Performance Support (APS) emerged, emphasizing usability for non-experts. Additionally, the rise of the internet during this period laid the groundwork for modern e-learning systems, offering organizations a broader range of training options tailored to specific outcomes.
Reference list
Torraco, R.J. (2016). Early History of the Fields of Practice of Training and Development and Organization Development. [online] Sage Journals Home. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/stoken/rbtfl/pVidtvVp8xWME/full.